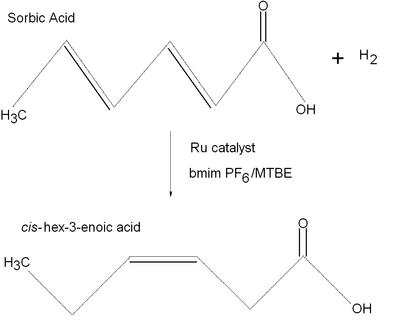
This reaction is an example of the catalytic hydrogenation of an acid in an ionic liquid similar to the reagents sodium metal/liquid ammonia discussed in lecture. This particular reaction has sorbic acid and hydrogen gas reacting with a ruthenium catalyst and a biphasic 1-butyl-3-methyl imidazolium hexafluorophosphate (bmimPF6)/methyl tert-butyl ether (MTBE) system to create cis-hex-3-enoic acid. The above reaction occurs with ~85% selectivity. The author of this paper was examining enantioselective hydrogenation in ionic liquids because this mechanism could provide a means for facile recycling of metal complexes of expensive chiral ligands. The author also studies some hydrogenation reactions that lead to the precursor of the antiinflammatory drug ibuprofen, the active ingredient in Advil.
For the full text click here.
No comments:
Post a Comment